Table of Contents
ToggleIt is one of the most powerful tools available today and still has much to offer it was created by satoshi nakamoto. It has completely changed the way we do things, making the world a more interconnected place, protecting our privacy and security. A technology that goes beyond the economy and extends to all areas of society, from music or politics to health or bureaucracy. Find out what is blockchain and how it works.
Something that not many people know is that blockchain technology was designed several years ago, in 1991. The pioneers, Stuart Haber and W. Scott Stornetta, published the document “How to Time-Stamp a Digital Document” that many consider the prelude to blockchain technology. However, it didn’t become popular until the emergence of bitcoin and despite its integration there are still certain doubts about if bitcoin is safe and anonymous.
What is blockchain?
The concept “blockchain” defines its operation very well.
Blockchain is a technology that enables the transfer of digital data under complex coding, in a secure way. How? By creating a distributed account book in a computer network, without having a central server or database, and whose advances arise from the consensus between the parts that make up the network.
There is talk of “blockchain” because in the large accounting book that this technology creates all transactions are written down in blocks connected to each other. However, each transaction needs to be validated by several users (independent nodes) of the network so that the block ends up being registered in the account book.
Consensus, encryption and decentralization allow the blockchain to have very high security standards compared to other technologies.

How does blockchain technology work?
First, software is needed that allows computers to create the network that operates the blockchain in a distributed way. The fact of not having a centralized server located means that it is a distributed network and that all the information is available on all the computers connected to the same blockchain.
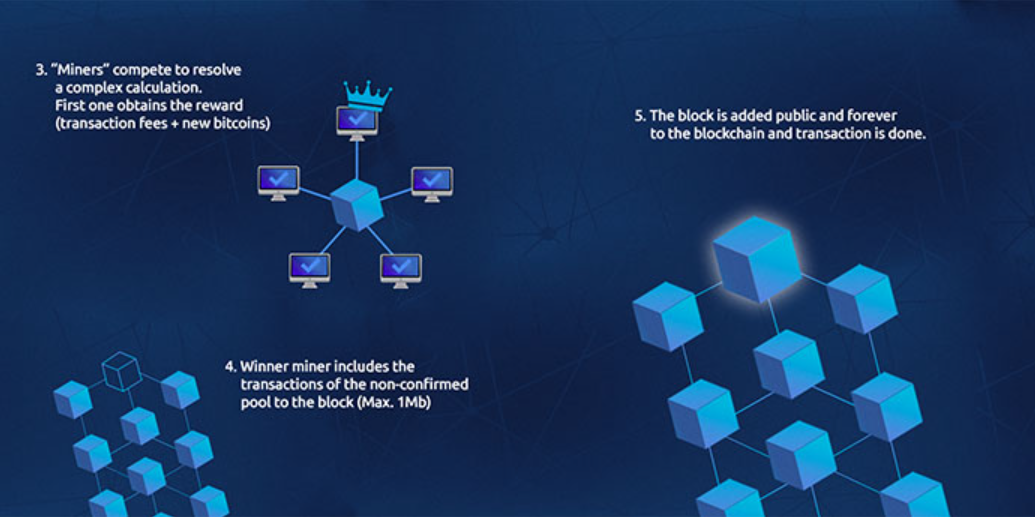
From time to time, the different transactions that make up a block are verified, so the block is validated by the independent nodes of the network (the famous mining). Each block contains:
-Multiple validated transactions
-Information regarding the block itself
-Information about its connection with the previous block and with the later one (hash).
Thus, each block has a specific and unalterable place within the chain and cannot be modified. The chain is always available on all connected computers, so there is no risk of losing data in case the network falls.
Infographic: How does blockchain technology work?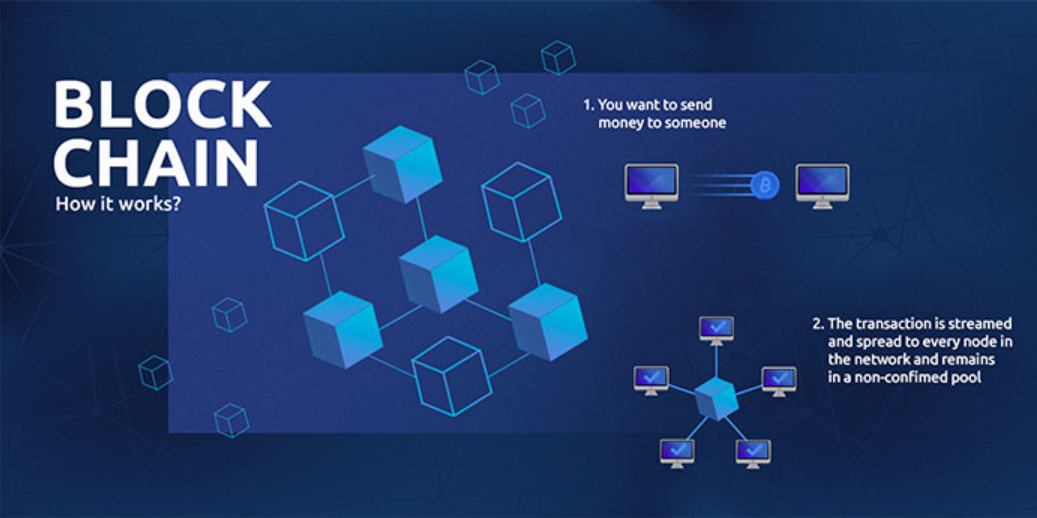
Open-source blockchains, such as Bitcoin or Ethereum, are accessible to anyone and, therefore, the information is public. Yes, when you buy cryptocurrencies online, blockchain technology is also present, this area is no exception.
Those who know well what blockchain is and how it works, know the value that this technology brings to all fields of society: Internet voting, collaborative economics, notary services, the insurance sector, digital marketing, finance and a long etcetera.
Is Blockchain Secure?
Blockchain aims at security and trust, which it handles in several ways. As the first the block is added in a linear and chronological way in the blockchain network. That is, it is always added at the end of the blockchain which increases the amount of blocks in the chain, if you look at the blockchain they have a position in the chain that is called “height”.
When a block is added to the end of the block chain, it’s almost impossible to go back and alter the content of the previous block. This is because each block contains its own cryptographic hash, along with it. Hash codes are created by a math function that turns digital information into a string of numbers and letters. If that information is edited in any way, the hash code changes as well.
This is very important for security because if a hacker tries to edit your transaction so that you have to pay for a transaction twice. When you do this and edit the payment amount of the transaction, the hash of the block will change. The hacker will have to update the block to cover your information which will cause you to have to update it again and so on.
In order for a hacker to change the information in a block, he needs to change the information in each subsequent block in the block chain. Doing this would require an impossible amount of hashes for the computers we have today since there is no such thing as this amount of computing power. This means that once a block is added to the block chain, it becomes very difficult to edit and impossible to remove.
When it comes to trust, blockchain based networks have implemented a test for computers that want to join and help add blocks to the block chain. The tests, called “consensus models,” require users to “prove” themselves before they can participate in a blockchain network. One of the most common examples employed by Bitcoin is called “proof of work.
This system of proof of work, makes computers check that they have done a job in solving a complex computer math problem. If a computer solves one of these problems, it is chosen to add a block to the block chain. But this process of adding blocks to the chain of blocks.
Which in the world of cryptos is called mining, is not easy to do. The probability of solving one of these problems is approximately between 1 and 17 billion. To do these computers need a lot of resources and energy.
This Proof of Work is not an impossible barrier for hackers to break through, but it makes them somewhat useless because if a hacker wanted to coordinate an attack on the block chain.
He would need to control more than 50% of all the computing power in the block chain in order to dominate the other participants in the network. Because the block chain in this case of bitcoin is so large it is certain that an attack of 51% will not be successful as it is very likely to be impossible.
Blockchain’s Practical Application
Blocks on the blockchain save the data of the monetary transactions. But this makes blockchain actually a fairly reliable way to store data about other types of transactions. The blockchain technology can be used to store different types of data such as property changes or even voting information.
There is speculation that companies are slowly applying or already have applied a blockchain system in their companies to improve their production.
Here are two of the most popular block chain applications being explored today.
Bank Use
We do think that the industry that would most benefit from the integration with blockchain in its commercial operations in banking would be this one. Financial institutions are only operational during business hours, five days a week. Making a deposit on a Friday at 6 pm is not possible and you would have to wait until Monday morning for the money to arrive in your account.
Even when depositing during business hours, the transaction may take one to three days to verify due to the large volume of transactions that banks process. Blockchain does not have these limitations since it is a service that is always active, very fast in its peer to peer transactions and also sometimes it is delayed a little because of the great amount of transactions that it has to verify.
By integrating Blockchain with the banks, consumers can see that their transactions will be processed in only 10 to 5 minutes, which is the time it takes to add a block to the blockchain, regardless of the day or time of the week in which the transaction is made. With blockchain, banks would also have the facility to exchange assets between banking institutions in a fast and secure manner. When a settlement or compensation is made, it can take up to three days or more depending on the banks.
These types of transactions, even if they last only a few days, can carry significant transaction fees and risks for both the banks and your bank account. It is estimated that if blockchain applications were used by banks, they could save up to 16 million in banking and insurance fees charged year over year, which could also be reflected in credit cards fees.
Use in Smart Contracts
A smart contract is a computer code that can be built into the blockchain to facilitate, verify, or negotiate a contract agreement. Smart contracts operate under a set of conditions that users agree to. When those conditions are met, the terms of the agreement are automatically carried out.